NEB computer science 2081 questions with solutions
NEB-GRADE XII
2081 (2024)
Computer Science Sub.Code:
4281
(New course)
(For the regular and grade increment students whose first two digits of registration number starts from 78, 79 and 80)
Multiple Choice Questions [9x1=9]
Rewrite the correct option of each question in your same
answer sheet.
Group 'A'
1. Which one of the followings given statement correct?
A) Select * from enp where eopid
= 103;
B) Select from enp where eopid =
103;
C) Select eopid where enp = 103
from emp;
D) Select eopid where eopid = 103
and table = emp;
2. Which database system normally offers better performance
for geographically dispersed users ?
A) Centralized database system B) Distributed database system
C) NoSQL database system D) Relational database system
3. Which of the following is an example of a public IPV4
address?
A) 192.168.1.1 B)
172.16.10.1
C) 10.10.10.10 D)
203.0.113.10
4. What is the correct syntax for a 'for-loop' in
JavaScript?
A) for (var i=0; i<5; i++){} B) for (i=0;
i<5; i++) {}
C) for (var i=0; i<5) {} D) for
(var i<5; i++) {}
5.Which PHP function is commonly used to execute SQL queries
on a database connection established using mysqli extension ?
A) mysqli_query() B)
pdo_query()
C) mysql_query() D)
pgsql_query()
6.What is the correct syntax to declare a structure in C?
A) struct { } B) define struct {}
) struct [ ] D) struct <name> {}
7. In C, which operator is used to get the address of a
variable?
A)* B) &
C)-> D).
8. Which OOP feature allows a class to inherit properties
and behavior from another class?
A) Inheritance B)
Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism D)
Abstraction
9. Which model of SDLC is characterized by a linear
progression of phases from requirements gathering to maintenance ?
A) Waterfall model B) Agile model
C) Spiral model D) RAD model
Group
'B'
Short answer questions [5x5=25]
10. Evaluate the advantages of DBMS compared to traditional file-based data storage systems.
OR [5]
How does Second Normal Form (2NF)
differ from First Normal Form (INF), and what are the key benefits of achieving
2NF in database design? Explain. [2+3]
11. Write a JavaScript function
that checks if a number is even or odd and print the result. [1+4]
OR
What is purpose of the
mysqli_connect() function in PHP? Describe its usage and parameters. [2+3]
12. Write short note on class and
object in OOPS with a real-word example.
[2.5+2.5]
13. How do various requirement
gathering techniques help in achieving a careful grasp of user needs and system
requirements during SDLC's analysis phase? [5]
14. Give five examples of AI applications in the education. [5]
Group
'C'[12×8-16]
Long answer questions
15. How does the star network
topology differ from the bus network topology in terms of its architectural
layout and data transmission methodology in modern computing environments?[8]
16. Write a C program that uses structures to
represent details of five books title, author, publisher and price) and prints
them out. [8]
OR
Discuss the concept of binary file
handling in C programming and explain how putw() and getw() functions
facilitate binary input/output operations. Give examples. [8]
Solutions:
NEB computer science 2081 questions with solutions
NEB-GRADE XII
2081 (2024)
Computer Science Sub.Code: 4281
(New course)
(For the regular and grade increment students whose first two digits of registration number starts from 78, 79 and 80)
Multiple Choice Questions [9x1=9]
Rewrite the correct option of each question in your same answer sheet.
Group 'A'
1. Which one of the followings given statement correct?
A) Select * from enp where eopid = 103;
B) Select from enp where eopid = 103;
C) Select eopid where enp = 103 from emp;
D) Select eopid where eopid = 103 and table = emp;
2. Which database system normally offers better performance for geographically dispersed users ?
A) Centralized database system B) Distributed database system
C) NoSQL database system D) Relational database system
3. Which of the following is an example of a public IPV4 address?
A) 192.168.1.1 B) 172.16.10.1
C) 10.10.10.10 D) 203.0.113.10
4. What is the correct syntax for a 'for-loop' in JavaScript?
A) for (var i=0; i<5; i++){} B) for (i=0; i<5; i++) {}
C) for (var i=0; i<5) {} D) for (var i<5; i++) {}
5.Which PHP function is commonly used to execute SQL queries on a database connection established using mysqli extension ?
A) mysqli_query() B) pdo_query()
C) mysql_query() D) pgsql_query()
6.What is the correct syntax to declare a structure in C?
A) struct { } B) define struct {}
) struct [ ] D) struct <name> {}
7. In C, which operator is used to get the address of a variable?
A)* B) &
C)-> D).
8. Which OOP feature allows a class to inherit properties and behavior from another class?
A) Inheritance B) Encapsulation
C) Polymorphism D) Abstraction
9. Which model of SDLC is characterized by a linear progression of phases from requirements gathering to maintenance ?
A) Waterfall model B) Agile model
C) Spiral model D) RAD model
Group 'B'
Short answer questions [5x5=25]
10. Evaluate the advantages of DBMS compared to traditional file-based data storage systems.
Ans:-
Here are some advantages of DBMS over traditional file based system.
1. Redundancy is reduced
File-based systems: Often store the same data in multiple files (redundancy).
-
DBMS: Uses centralized control to minimize duplication through normalization and relational structure.
OR [5]
How does Second Normal Form (2NF) differ from First Normal Form (INF), and what are the key benefits of achieving 2NF in database design? Explain. [2+3]
Ans:-
To understand the difference between 1NF and 2NF, lets understand about them in detail with example.
1NF:
A table is said to be in 1NF if it satisfies the following conditions.
1. If it contains no repeating fields such as phone1,phone2 in different columns.
2.If each column contains indivisible data i.e atomic or single valued data.
| StudentID | Name | Subjects |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Ram | Math, Science |
| 102 | Sita | English, Nepali |
| StudentID | Name | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Ram | Math |
| 101 | Ram | Science |
| 102 | Sita | English |
| 102 | Sita | Nepali |
| StudentID | CourseID | StudentName | CourseName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C101 | Ram | Math |
| 2 | C102 | Sita | Science |
Here StudentID+CourseID is being primary key.In this table the filed CourseName is dependent on CourseID and StudentName is depedent on StudentID, not fully on both. So there is being partial dependency.
Now breaking this into tables such as
studentcourse
| StudentID | CourseID |
|---|---|
| 1 | C101 |
| 2 | C102 |
students
| StudentID | StudentName |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ram |
| 2 | Sita |
courses
| CourseID | CourseName |
|---|---|
| C101 | Math |
| C102 | Science |
So these tables are in 2NF.
key benefits of 2NF:
1.Eliminate partial dependency
2.reduces data redundancy
3.optimizes storage
4. improves query efficiency
11. Write a JavaScript function that checks if a number is even or odd and print the result. [1+4]
Ans:-
<script>
function checkEvenOrOdd()
{
let number = parseInt(prompt("Enter a number:"));
if (number % 2 === 0)
{
console.log(number + " is even.");
}
else
{
console.log(number + " is odd.");
}
}
checkEvenOrOdd();
</script>
OR
What is purpose of the mysqli_connect() function in PHP? Describe its usage and parameters. [2+3]
Ans:-
The mysqli_connect() function is used to establish a connection to a MySQL database using the MySQLi (MySQL Improved) extension in PHP.
Syntax:
mysqli_connect(host, username, password, database, port, socket);
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| host | The hostname or IP address of the MySQL server (e.g., "localhost"). |
| username | MySQL username (e.g., "root"). |
| password | Password for the MySQL user. Mostly it is empty. |
| database | Name of the database to connect to. |
Example: |
$connection = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "", "school");
if (!$connection) {
die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
echo "Connected successfully";
?>
12. Write short note on class and object in OOPS with a real-word example. [2.5+2.5]
Ans:-
Class and Object in OOPS
In Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), classes and objects are fundamental concepts.
-
Class:
A class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that objects created from the class will have.-
Example: A Car class might have properties like
color,model, andspeed, and methods likeaccelerate()andbrake().
-
-
Object:
An object is an instance of a class. It represents an entity with specific values for the class’s attributes and can perform actions defined by the class’s methods. -
Example: A specific car like a "red Ferrari" is an object of the Car class.
13. How do various requirement gathering techniques help in achieving a careful grasp of user needs and system requirements during SDLC's analysis phase? [5]
Ans:
During the Analysis Phase of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), various requirement gathering techniques help in accurately understanding user needs and system requirements. Here's how they contribute:
-
Interviews
-
Directly engaging with stakeholders helps collect specific requirements, clarify user expectations, and uncover potential issues early on.
-
-
Surveys and Questionnaires
-
Efficient for gathering feedback from a large number of users, identifying common needs, preferences, and concerns.
-
-
Use Cases and User Stories
-
These techniques describe how users interact with the system, ensuring a focus on user-centric features and functionality.
-
-
Workshops
-
Collaborative sessions with stakeholders allow for deeper discussions, prioritization of requirements, and consensus-building on key features.
-
-
Prototyping
-
Developing prototypes helps stakeholders visualize the system early, refine requirements, and identify missing or misunderstood features.
-
14. Give five examples of AI applications in the education. [5]
Ans:
Artificial Intelligence:
AI (Artificial Intelligence) refers to the capability of machines or software to simulate human intelligence. It involves the development of systems that can perform tasks such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, and decision-making by analyzing data and adapting over time.
Its applications in the education are given below.
-
Personalized Learning
AI-driven systems analyze student performance and tailor content to individual learning styles and paces, helping students grasp concepts more effectively. -
Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI tutors provide real-time feedback and personalized assistance to students, helping them with subjects like math, science, and language by identifying areas of difficulty. -
Automated Grading
AI can grade assignments and exams, especially for objective questions like multiple choice, short answers, and essays, reducing teachers' workload and providing faster feedback. -
Virtual Learning Assistants
AI-powered chatbots or virtual assistants help students navigate courses, answer questions, and offer resources, making learning more accessible. -
Predictive Analytics
AI uses data to predict student outcomes, such as identifying students at risk of underperforming, allowing for timely interventions and support.
Group 'C'[12×8-16]
Long answer questions
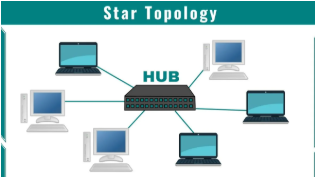
15. How does the star network topology differ from the bus network topology in terms of its architectural layout and data transmission methodology in modern computing environments?[8]
ans:-
Star topology:
In a Star Topology, all devices (nodes) are connected to a central hub or switch. Communication between devices always passes through this central device.
Transmission methodology:
In a modern transmission methodology, each device sends data to a central hub or switch, which then forwards it to the intended destination device. Unlike older shared communication systems, modern networks utilize switched communication that operates on a point-to-point basis. This approach significantly reduces data collisions, as each connection is given a dedicated communication path within the switch. As a result, there is minimal interference between devices.Advantages of Star Topology
-
Easy to Manage and Troubleshoot
-
Since each device is connected individually to the central hub/switch, it's easy to detect and fix issues.
-
-
Fault Isolation
-
Failure in one cable or device doesn't affect the rest of the network.
-
Disadvantages of Star Topology
-
Dependency on Central Hub/Switch
-
If the hub or switch fails, the whole network becomes inoperative.
-
-
Higher Cost
-
Requires more cable length and additional hardware like switches or hubs, making it costlier than bus topology.
-
Bus topology:-
Bus topology is a network setup where all devices (nodes) are connected to a single central cable, called the bus or backbone. Data sent by a device is broadcasted along this cable and received by all connected devices.
Transmission mechanism:-
In broadcast transmission, data travels both ways on a shared bus, where all devices receive it, but only the intended one accepts it. The CSMA/CD protocol manages this by checking if the bus is free before sending. If two devices transmit at once, a collision occurs, prompting both to wait randomly before retrying.
Advantages of Bus Topology
-
Cost-Effective
-
Requires less cabling compared to star topology. No need for extra devices like switches or hubs.
-
-
Easy to Set Up
-
Simple layout and minimal hardware make it easy to install and configure, especially for small networks.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
-
Limited Scalability
-
Adding many devices can slow down the network and increase chances of collisions.
-
-
Difficult Fault Detection
-
If a problem occurs, it's hard to identify the exact point of failure in the bus.
-
16. Write a C program that uses structures to represent details of five books title, author, publisher and price) and prints them out. [8]
OR
Discuss the concept of binary file handling in C programming and explain how putw() and getw() functions facilitate binary input/output operations. Give examples. [8]
Why Binary Files?
-
Faster access and processing.
-
Stores exact memory representation (good for structs).
-
Useful for multimedia, database, or large data applications
putw() and getw() are simple functions used to write and read integers to/from a binary file. They are used for binary I/O and work directly with integer values.