NEB 2080 computer science(regular)
Group 'B'
Short answer questions 5x5=25
Long answer questions
Group 'C' 8x2-16
NEB 2080 computer science(supplementary)
Sub.Code: 4281'B'
NEB-GRADE XII 2080 (2023)
Computer Science Time: 2 hrs.
Full Marks: 50
Grade Increment (Supplementary) Examination
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figures in the margin indicate full marks.
Very short answer questions.9x1=9
Group 'A'
1. Which SQL keyword is used to retrieve data from a table?
a) SELECT
c) WHERE
b) FROM
d) JOIN
2. Which of the following principle apply to 2NF?
a) A table must have a primary key
b) All non-key attributes must be dependent on the primary key
c) All attributes must be atomic
d) A table must have at least more than two attributes.
3. Which of the following is a device that connects two or more networks and can filter and forward network traffic based on its destination address?
a) Switch c) Hub b) Router d) Modem
4. Which JavaScript function use to text input?
a) alert() b) prompt() c) confirm() d) console.log()
5. Which of the following PHP functions is used to connect to a MySQL database?
a) mysql_connect()
c) pdo_connect()
b) mysqli_connect()
d) db_connect()
6. What is the correct way to open a file named "data.txt" in C for reading?
a) fopen("data.txt", "r");
b) fopen("data.txt", "w");
c) fopen("data.txt", "a");
d) fopen("data.txt", "rb");
7. Which of the following concepts in object-oriented programming refers to binding data and function into a single unit.
a) Encapsulation
c) Polymorphism
b) Abstraction
d) Inheritance
8. What does the term "QA" stand for in the software development process?
a) Quality Assurance
c) Quality Assessment
b) Quality Analysis
d) Quantity Assurance
9. What type of communication technology is commonly used in IoT devices?
a) Wi-Fi
b) Bluetooth
c) Zigbee
d) All of the above
Group 'B'
Short answer questions 5x5=25
10. Describe the second normal form (2NF) with an example.
OR
What are the importance of database security in database management systems? Describe.
11. How do you add an event handler in JavaScript? Give an example.
OR
Explain the database connection PHP function for MySQL.
12. Describe the object and class in OOPS with an example.
13. Explain the agile software development methodology in brief.
14. Give any five examples of AI related applications.
Long answer questions.2x8=16
Group 'C' 4+4
15. Compare the bus and star network topology. Which of the network cable is suitable to design star topology in the school's network? Justify.
16. Write a program to store five employees' records (EID, Name, post and I C department) and display them using structure.
OR
Describe file handling modes on C. Write a C program to create and write data into a file. 4+4
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Solutions
NEB 2080 computer science(regular)
Group 'B'
Short answer questions 5x5=25
Students table might store information about students, with each row representing one student and each column representing details like name, age, or department.| StudentID | Name | Age | DeptID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ram | 18 | D1 |
| 2 | Sita | 19 | D2 |
| 3 | Hari | 20 | D1 |
1) Emphasis is on data rather than procedures or algorithms.
2) Programs are divided into what are known as objects.
3) Data structures are designed such that characterize the objects.
4) Functions that operate on the data are tied together in the data structure.
5) Data is hidden and cannot be accessed by external functions.
6) Objects may communicate with each other through functions.
7) New data and functions can be easily added whenever necessary.
8) Follows bottom-up approach in program design.
1) Emphasis is on doing things(algorithms).
2) Large programs are divided into smaller programs known as functions.
3) Most of the functions share global data.
4) Data more openly around the system from function to function.
5) Functions transform data from one form to another.
6) Employs a top-down approach in program design.
Examples: C, Pascal, early BASIC.
System Testing plays a crucial role in the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) because it ensures that the software functions as expected and meets both the technical and business requirements. It's the phase where the entire system is tested as a whole to check for any issues, bugs, or gaps in functionality before the system is released to the users.
Below are the key reasons why System Testing is important:
1. Ensures Quality and Reliability
2. Identifies Bugs and Defects
3. Validates Business Requirements
4. Verifies Compatibility
5. Performance and Load Testing
Disadvantages:
1.Data Security and Privacy Concerns:
-
Storing sensitive data on remote servers raises concerns about data breaches, hacking, or unauthorized access.
2.Downtime and Service Interruptions:
-
Cloud services are susceptible to service outages. If the cloud provider experiences a failure, users may be unable to access their data or services until the issue is resolved.
Long answer questions
Group 'C' 8x2-16
Guided (Wired Media):
Guided media refers to physical transmission mediums where data is transmitted via wires or cables, which guide the signal along a specific path. This type of medium requires a physical connection between devices in the network.
-
Examples:
-
Twisted Pair Cable (e.g., Ethernet cables used in local area networks).
-
Coaxial Cable (used in cable internet connections).
-
Fiber Optic Cable (used for high-speed, long-distance communication).
-
-
Characteristics:
-
Physical medium: Data is transmitted through physical cables.
-
Limited distance: The data transmission distance is limited by the type of cable used.
-
Stable connection: Provides more stable and reliable communication compared to wireless media.
-
Higher security: Since the signals are confined to the physical medium, there is less chance of unauthorized interception.
-
Requires installation: Physical installation of cables is necessary, which can be time-consuming and costly.
-
Unguided (Wireless Media):
Unguided media refers to the transmission of data through air or space using electromagnetic waves, without the need for physical cables or wires. It is often referred to as wireless communication.
-
Examples:
-
Radio Waves (used in broadcast radio and wireless LANs).
-
Microwaves (used in satellite communications and point-to-point networks).
-
Infrared (IR) (used in remote control devices).
-
Wi-Fi (used in wireless networking for connecting devices).
-
-
Characteristics:
-
No physical medium: Data is transmitted through the air using electromagnetic signals.
-
Greater range: Wireless communication allows data transmission over larger areas, especially with advanced technologies like satellite or cellular networks.
-
Mobility: Devices can move freely within the coverage area without being restricted by physical cables.
-
Prone to interference: Wireless signals can be affected by various factors such as weather conditions, physical obstructions, and other devices operating on the same frequency.
-
Lower security: Wireless signals are more vulnerable to interception, and extra security measures such as encryption are needed to prevent unauthorized access.
-
A pointer is a variable that stores the memory address of another variable. Instead of holding a data value directly, a pointer "points to" the location in memory where the value is stored.
In C, pointers are declared using the asterisk (*) symbol.
Example: int *p; //p is a pointer
- They allow efficient memory management by enabling dynamic allocation and deallocation of memory during runtime.
- Pointers also lead to faster program execution as they offer direct access to memory locations.
- One key advantage is that pointers support call by reference, allowing functions to modify the actual values of variables passed to them.
- They are essential in implementing advanced data structures such as linked lists, trees, stacks, and queues.
Structure:-
Structure is a user defined data type available in C that allows to combine data items of different kinds.
Structures are used to represent a record. Suppose we want to keep track of your books in a library. we might want to track the following attributes about each book −
Title
Author
Subject
Book ID
For this, structure is helpful.
Features:-
We can copy items of one structure to another using = operator.
We can use structure in nested form.
We can pass the entire structure to a function.
We can create an array for a given structure.
Syntax:
struct tag name
{
Data type member 1;
Data type member2;
} variable;
Example:
struct book
{
Char b_name[100];
Char b_authro[100];
float b_price;
}v;
NEB 2080 computer science(supplementary)
Sub.Code: 4281'B'
NEB-GRADE XII 2080 (2023)
Computer Science Time: 2 hrs.
Full Marks: 50
Grade Increment (Supplementary) Examination
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figures in the margin indicate full marks.
Very short answer questions.9x1=9
Group 'A'
1. Which SQL keyword is used to retrieve data from a table?
a) SELECT
c) WHERE
b) FROM
d) JOIN
2. Which of the following principle apply to 2NF?
a) A table must have a primary key
b) All non-key attributes must be dependent on the primary key
c) All attributes must be atomic
d) A table must have at least more than two attributes.
3. Which of the following is a device that connects two or more networks and can filter and forward network traffic based on its destination address?
a) Switch c) Hub b) Router d) Modem
4. Which JavaScript function use to text input?
a) alert() b) prompt() c) confirm() d) console.log()
5. Which of the following PHP functions is used to connect to a MySQL database?
a) mysql_connect()
c) pdo_connect()
b) mysqli_connect()
d) db_connect()
6. What is the correct way to open a file named "data.txt" in C for reading?
a) fopen("data.txt", "r");
b) fopen("data.txt", "w");
c) fopen("data.txt", "a");
d) fopen("data.txt", "rb");
7. Which of the following concepts in object-oriented programming refers to binding data and function into a single unit.
a) Encapsulation
c) Polymorphism
b) Abstraction
d) Inheritance
8. What does the term "QA" stand for in the software development process?
a) Quality Assurance
c) Quality Assessment
b) Quality Analysis
d) Quantity Assurance
9. What type of communication technology is commonly used in IoT devices?
a) Wi-Fi
b) Bluetooth
c) Zigbee
d) All of the above
Group 'B'
Short answer questions 5x5=25
10. Describe the second normal form (2NF) with an example.
Ans:-
| StudentID | CourseID | StudentName | CourseName |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C101 | Ram | Math |
| 2 | C102 | Sita | Science |
Here StudentID+CourseID is being primary key.In this table the filed CourseName is dependent on CourseID and StudentName is depedent on StudentID, not fully on both. So there is being partial dependency.
Now breaking this into tables such as
studentcourse
| StudentID | CourseID |
|---|---|
| 1 | C101 |
| 2 | C102 |
students
| StudentID | StudentName |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ram |
| 2 | Sita |
courses
| CourseID | CourseName |
|---|---|
| C101 | Math |
| C102 | Science |
So these tables are in 2NF.
key benefits of 2NF:
1.Eliminate partial dependency
2.reduces data redundancy
3.optimizes storage
4. improves query efficiency
OR
What are the importance of database security in database management systems? Describe.
Ans:-
Database security plays a crucial role in protecting the data stored in a database management system (DBMS). As databases often contain sensitive, valuable, or confidential information, it is essential to ensure that only authorized users can access and manipulate the data.
The key reasons why database security is important are:
Protects Sensitive Data:
Database security ensures that personal, financial, or confidential information (such as user credentials, bank details, or organizational secrets) is protected from unauthorized access, leaks, or breaches.-
Prevents Data Loss or Corruption:
Security mechanisms such as backup and recovery systems help protect data from being accidentally deleted, modified, or corrupted due to malicious activities or software bugs. -
Maintains Data Integrity:
Security ensures that the data remains accurate and consistent over its lifecycle. It prevents unauthorized changes that could lead to data tampering or integrity loss. -
Ensures Access Control:
Through authentication and authorization techniques, security systems control who can access the database and what actions they are allowed to perform (such as read, write, or delete). -
Protects Against Cyber Threats:
Database security protects against various threats like SQL injection, malware, phishing, and ransomware attacks, which can exploit vulnerabilities to steal or destroy data.
11. How do you add an event handler in JavaScript? Give an example.
Ans:-
In JavaScript, an event handler is a function that runs when a specific event occurs (like a button click, mouse movement, key press, etc.).
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Event Handler Example</title> </head> <body> <button onclick="myBtn()">Click Me</button> <script> function myBtn() { alert("Button was clicked!"); } </script> </body> </html>
OR
Explain the database connection PHP function for MySQL.
Ans:-
To connect a PHP script with a MySQL database, we commonly use the mysqli_connect() function. This function allows PHP to communicate with the MySQL server.
Syntax:
mysqli_connect(servername, username, password, dbname);
servername: Usually "localhost" if the database is on the same server.
Example:
<?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "root"; $password = ""; $database = "student"; $conn = mysqli_connect($servername, $username, $password, $database); if (!$conn)
{ die("Connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error()); } echo "Connected successfully"; ?>
12. Describe the object and class in OOPS with an example.
Ans:-
Class and Object in OOPSClass:
Class and Object in OOPS
A class is a blueprint or template for creating objects. It defines the properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that objects created from the class will have.
Example: A Car class might have properties like
color,model, andspeed, and methods likeaccelerate()andbrake().
An object is an instance of a class. It represents an entity with specific values for the class’s attributes and can perform actions defined by the class’s methods.
Example: A specific car like a "red Ferrari" is an object of the Car class.
Ans:-
Agile development model:Agile software development is a modern and flexible approach to building software that emphasizes incremental progress, collaboration, and adaptability. Unlike traditional methods (like the Waterfall model), Agile breaks the project into small, manageable parts called iterations or sprints, usually lasting 1–4 weeks.
Each sprint results in a working version of the software, allowing teams to get frequent feedback, make changes quickly, and deliver high-quality products faster. Agile promotes continuous improvement, teamwork, and customer involvement throughout the development process.
Key Principles of Agile:
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
- Responding to change over following a plan
- Working software over comprehensive documentation
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
-
Faster delivery of features
-
Increased customer satisfaction
-
Greater flexibility and adaptability
-
Better risk management
-
Improved team communication
14. Give any five examples of AI related applications.
Ans:-1. Virtual Assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant)
These AI-powered tools understand voice commands and perform tasks like setting reminders, playing music, answering questions, or controlling smart home devices.
2. Recommendation Systems (e.g., Netflix, Amazon, YouTube)
AI analyzes user behavior and preferences to suggest relevant movies, products, or videos, enhancing user experience and increasing engagement.
3. Self-Driving Cars (e.g., Tesla Autopilot)
Autonomous vehicles use AI algorithms to process data from sensors, detect obstacles, follow traffic rules, and make driving decisions without human input.
4. Chatbots and Customer Support (e.g., Website Chat Support)
AI chatbots provide instant replies to customer queries, reducing the need for human agents and improving customer service efficiency.
5. Facial Recognition Systems
Used in security, smartphones, and surveillance, AI-powered facial recognition systems can detect and verify individuals based on facial features.
Long answer questions.2x8=16
Group 'C' 4+4
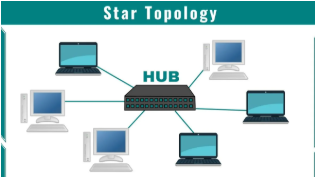
15. Compare the bus and star network topology. Which of the network cable is suitable to design star topology in the school's network? Justify.
Ans:-
comparison of star and bus topology:
Star topology:
In a Star Topology, all devices (nodes) are connected to a central hub or switch. Communication between devices always passes through this central device.
Transmission methodology:
In a modern transmission methodology, each device sends data to a central hub or switch, which then forwards it to the intended destination device. Unlike older shared communication systems, modern networks utilize switched communication that operates on a point-to-point basis. This approach significantly reduces data collisions, as each connection is given a dedicated communication path within the switch. As a result, there is minimal interference between devices.
Advantages of Star Topology
Easy to Manage and Troubleshoot
Since each device is connected individually to the central hub/switch, it's easy to detect and fix issues.
Fault Isolation
Failure in one cable or device doesn't affect the rest of the network.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
Dependency on Central Hub/Switch
If the hub or switch fails, the whole network becomes inoperative.
Higher Cost
Requires more cable length and additional hardware like switches or hubs, making it costlier than bus topology.
Bus topology:-
Bus topology is a network setup where all devices (nodes) are connected to a single central cable, called the bus or backbone. Data sent by a device is broadcasted along this cable and received by all connected devices.
Transmission mechanism:-
In broadcast transmission, data travels both ways on a shared bus, where all devices receive it, but only the intended one accepts it. The CSMA/CD protocol manages this by checking if the bus is free before sending. If two devices transmit at once, a collision occurs, prompting both to wait randomly before retrying.
Advantages of Bus Topology
Cost-Effective
Requires less cabling compared to star topology. No need for extra devices like switches or hubs.
Easy to Set Up
Simple layout and minimal hardware make it easy to install and configure, especially for small networks.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
Limited Scalability
Adding many devices can slow down the network and increase chances of collisions.
Difficult Fault Detection
If a problem occurs, it's hard to identify the exact point of failure in the bus.
SEcond part:-
The most suitable cable to design a star topology in a school network is the Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) cable, specifically Cat5e or Cat6.Cost-effective:
UTP cables are inexpensive and readily available, making them ideal for educational institutions with budget constraints.
Easy to Install and Manage:
UTP cables are lightweight and flexible, which makes them easier to install and maintain in classrooms and labs.
Good Speed and Performance:
Cat5e supports speeds up to 1 Gbps.
Cat6 supports up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, suitable for modern school networks with high-speed internet.
Compatibility with Networking Devices:
UTP cables are compatible with switches, routers, hubs, and other devices used in star topology.
Reliable for Indoor Use:
Since schools usually have controlled indoor environments, UTP cables work well without needing additional shielding.
16. Write a program to store five employees' records (EID, Name, post and I C department) and display them using structure.
Ans:-
#include<stdio.h> struct employees { int emp_id; char emp_name[100]; char emp_post[100]; char emp_dept[100]; }v[5]; int main() { int i; for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf("enter employee id\n"); scanf("%d",&v[i].emp_id); printf("enter employee name\n"); scanf("%s",&v[i].emp_name); printf("enter employee post\n"); scanf("%s",&v[i].emp_post); printf("enter employee department\n"); scanf("%s",&v[i].emp_dept); } printf("the records are:\n"); for(i=0;i<=4;i++) { printf("employee id=%d\n",v[i].emp_id); printf("employee name=%s\n",v[i].emp_name); printf("employee post=%s\n",v[i].emp_post); printf("employee department=%s\n",v[i].emp_dept); } return 0; }
OR
Describe file handling modes on C. Write a C program to create and write data into a file. 4+4
In C programming, file handling is done using different modes that define how a file should be opened — for reading, writing, or appending.
Here are the commonly used file modes:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
"r" | Opens a file for reading only. File must exist. |
"w" | Opens a file for writing only. If file exists, content is erased; if not, it is created. |
"a" | Opens a file for appending. Data is added at the end. File is created if it doesn't exist. |
"r+" | Opens a file for reading and writing. File must exist. |
"w+" | Opens a file for reading and writing. Erases content if file exists or creates a new one. |
"a+" | Opens a file for reading and appending. File is created if it doesn't exist. |